Multiphase Interactions
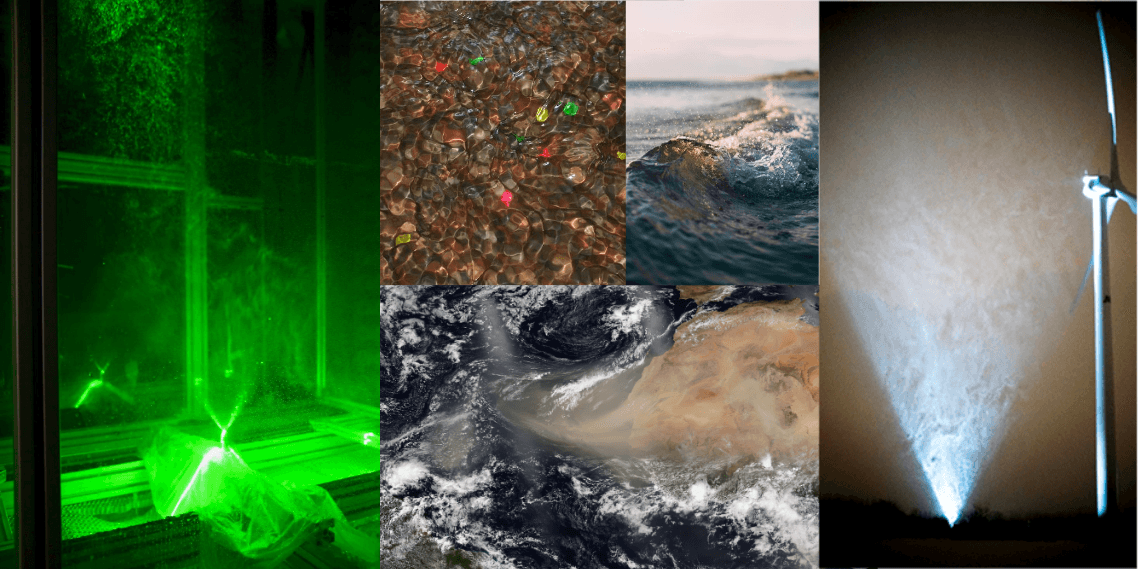
Multiphase flows are made up of a combination of the different states of matter, e.g. solids in liquids, liquids & gases, solids in gases, plasmas & gases, and so forth. These flows are all around us - wind driving the formation of ocean waves, debris flows and landslides occurring after a saturating rain, the bubbly flows associated with boat propellors,, sediment transport in streams and rivers - and the inherent complexity of these natural and engineered examples mean these flows are still very active topics of study. SAFL researchers use experimental facilities like CloudIA, the wind tunnel, and our assorted flumes and channels to help quantify the nature and behavior of different multiphase flows, while also using numerical techniques and simulations to better visualize these interactions and predict their behavior.
SAFL Affiliated Faculty
Roger Arndt
John Gulliver
Kimberly Hill
Jiarong Hong
Lian Shen
SAFL Researchers
Jeffrey Marr
Read more about SAFL multiphase related projects/research:
(filter "multiphase interactions" if needed)
MINUHET software tool available for practitioners to better assess temperature impacts of stormwater runoff in trout streams
Posted
MINUHET is a stand-alone software tool use to simulate the flow of stormwater surface runoff and its associated heat content through a small watershed. Interested practitioners can download the software on this page.
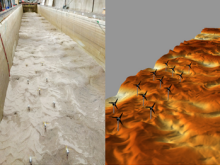
Harnessing clean energy from rivers through hydrokinetic turbine arrays
Posted
Hydrokinetic turbines are an emerging hydropower technology that take advantage of moving water currents to generate power.
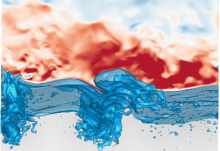
A numerical simulation of wind turbulence over breaking waves
Posted
Researchers studied the effect of waves breaking on the airflow above the waves. Research like this regarding wind and wave interactions can be used to improve ocean-atmosphere interaction models.

Mapping the evolution of barrier islands: Nature’s original coastline defense
Posted
Barrier islands act as natural barriers between the ocean and the mainland by blocking waves and resisting storm winds, giving protection to inland areas which are ecologically rich as well as economic hubs. As sea levels continue to rise with climate change, there is much concern about how rising seas will impact the ongoing evolution of barrier islands and the level of protection they afford inland coastlines.

Evaluating the effectiveness of pretreatment practices for rain gardens
Posted
The purpose of this project was to evaluate the effectiveness of different pretreatment devices in Minnesota. The objective was to gather quantitative data using a common method that will allow for comparisons across devices.

Evaluating permeable pavement as an alternative to road salt application
Posted
The Minnesota Department of Transportation tasked SAFL researchers with evaluating the use of unsalted permeable pavement in comparison to traditional impermeable salted pavement. Permeable pavement refers to a surface where water can infiltrate into pavement and ultimately become groundwater, rather than running off pavement into the stormwater system.
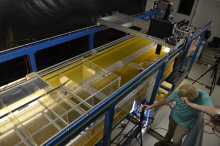
SAFL team designs flume to support juvenile fish studies
Posted
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) tasked SAFL researchers with the design of a race-track style flume, with the geometry and hydraulic conditions for early life stages of pallid sturgeon, an ancient but endangered fish species which historically inhabited the Missouri and lower Mississippi rivers

Channel belt evolution in braided rivers
Posted
Channel belts are wide corridors created by the movement of a river over time, as shown by geologic indicators such as abandoned channels and eroded valley margins. The purpose of this study was to evaluate how channel migration causes individual braided channel belts to grow using SAFL's main channel.

Broadway Pump Station Physical Model
Posted
After a 2011 flood caused extensive damage in Minot, North Dakota, MWH Americas, Inc. was hired to design a pumping station as part of the Mouse River Enhanced Flood Protection Plan, to pump stormwater over the river levee during flood events. The applied engineering team at the St. Anthony Falls Laboratory was then tasked to build a physical model of the proposed pumping station to identify and mitigate unanticipated/unacceptable flow patterns prior to construction.
Long-throated U-flume study
Posted
SAFL researchers built a scale model of a round-bottomed long-throated flume, in order to validate Winflume software for this specific flume geometry.
