Biological Engineering
Thirteen CEMS research groups, and four members of the CEMS graduate faculty, conduct pioneering research in biological engineering. With a strong foundation in physical, biological and mathematical sciences, Minnesota researchers study and engineer biological systems seeking solutions to vexing problems related to human health, energy production and the environment. From antibiotic technologies to stem cells, from biofuels to imaging technologies, from molecular biophysics to biomaterials, from biomedical devices to tissue engineering, an intellectually engaged community spans a wide spectrum of interests, exchanging ideas, sharing expertise and driving interdisciplinary solutions. See below for descriptions of focus areas within biological engineering, and the associated faculty, as well as a description of the UMN ecosystem for biological engineering research, common funding sources, and examples of recent publications.
Cancer Immunotherapy
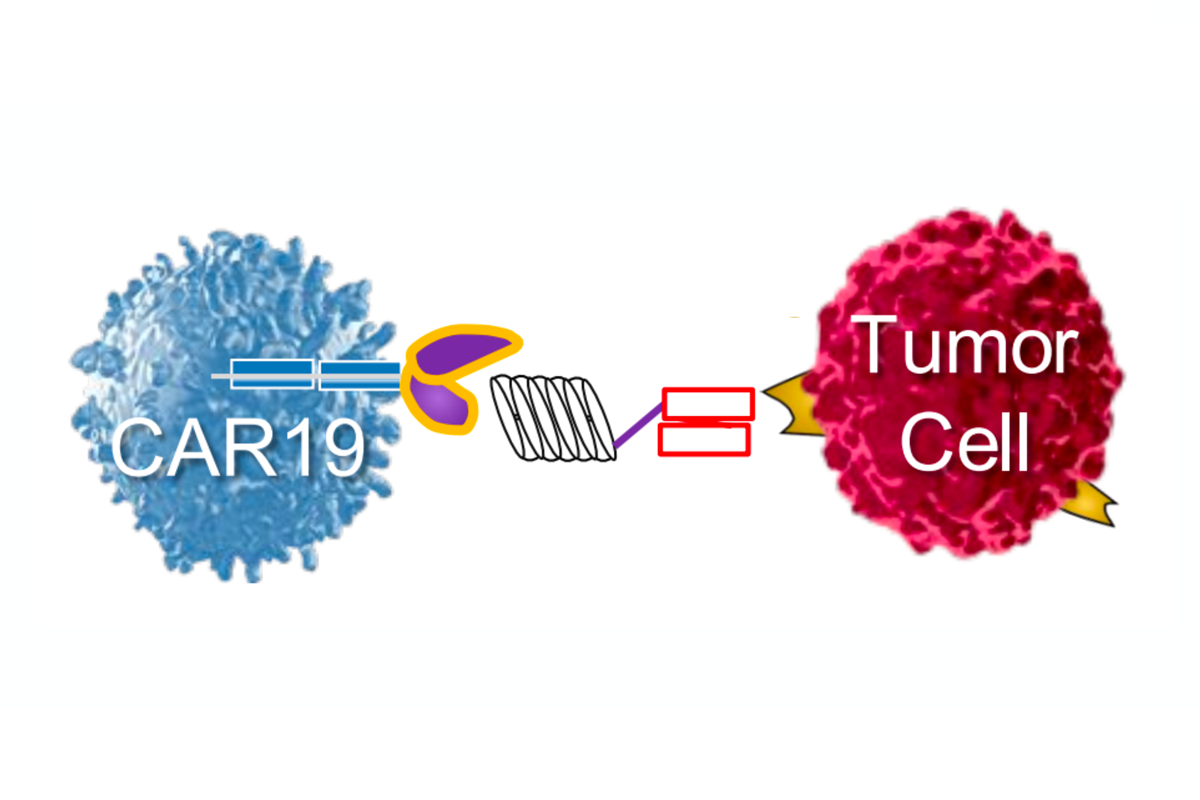
Harnessing the immune system has emerged as a powerful strategy to combat cancer although critical challenges remain. CEMS researchers are advancing technologies and fundamental understanding in cell therapy, molecular targeting, engineered cell production, and tumor-immune system interactions.
Related Faculty and Research Groups:
Biomaterials
The merger of the disciplines of chemical engineering and materials science within the same department has resulted in a wide variety of biomaterials-related applications. CEMS researchers are developing novel materials for biomanufacturing of cell-based therapies, drug delivery, and tissue engineering. In addition, there are many efforts to develop biomaterial therapeutics, with examples including nanomaterials for cancer therapy, block copolymers to repair the cell membrane, and lung surfactants. Additional efforts include synthesis and processing of sustainable polymers from biomass.
Related Faculty and Research Groups:
- Samira Azarin- Azarin Research Group
- Frank Bates- Bates Research Group
- Natalie Boehnke- Boehnke Research Group
- Michelle Calabrese - Calabrese Research Group
- Timothy Lodge- Lodge Research Group
- Theresa Reineke - Reineke Research Group
- Bob Tranquillo- Tranquillo Research Group
- Joseph Zasadzinski- Zasadzinski Research Group
Drug Delivery
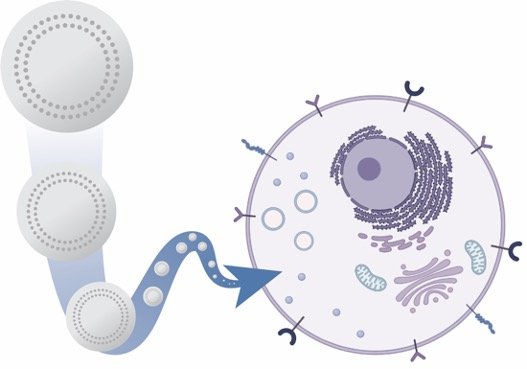
In the area of drug delivery, we apply chemical engineering approaches to develop new strategies to transport therapeutics through the body for a range of biomedical applications, including bacterial therapeutics for oral protein delivery and nanocarriers for targeted anticancer therapy delivery. We use materials science expertise to design and test new materials, ranging from protein therapeutics to nanoparticles, for improved transport properties, safety, and efficacy. This is a very collaborative and interdisciplinary research area both within the department and involving external collaborators, including the Chemistry and Biomedical Engineering Departments and the Masonic Cancer Center.
Related Faculty and Research Groups:
Computational & Systems Biology
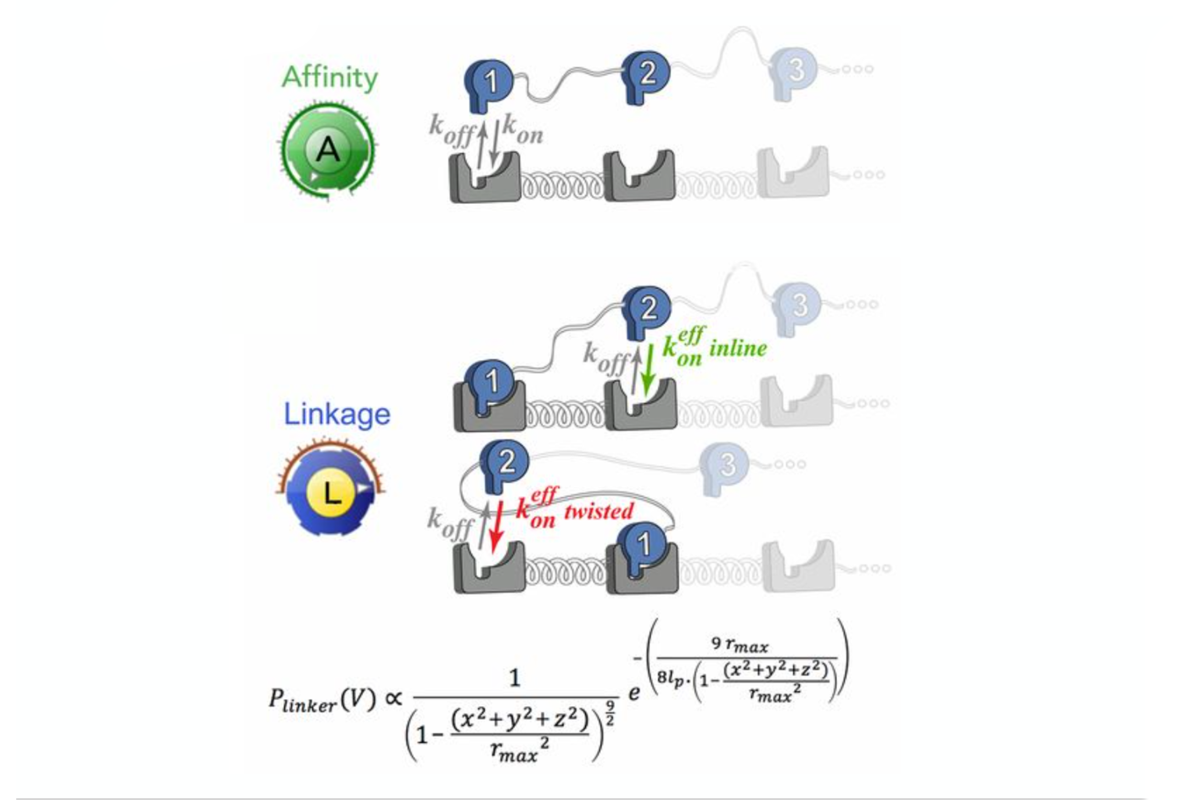
Computational biology combines modeling, simulations, and analytical tools for a quantitative understanding of biological systems. Systems biology allows us to apply these approaches to analyze interactions and relationships within biological systems. We use a combination of data science and systems analyses to model and study transport, evaluate biological responses to biomaterials and drug delivery systems, develop optimization and control strategies for metabolic engineering, regulate cellular decision-making, and achieve bioinformatics-guided protein design.
Related Faculty and Research Groups:
Fluid Dynamics/Biorheology
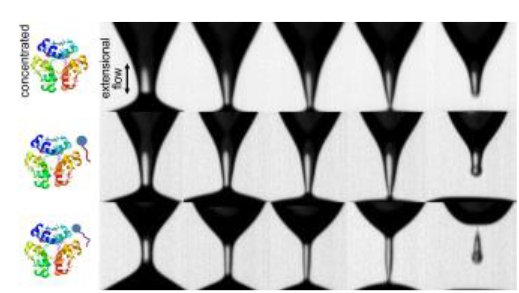
A variety of efforts in CEMS are focused on fluid dynamics in biological systems, including biorheology and injectable protein formulations, microfluidics for biosensing, and the study of active fluids such as bacterial suspensions.
Related Faculty and Research Groups:
Relevant Collaborative Partners and Core Facilities
The CEMS department (indicated by a star on the map below) is ideally situated within a larger biomedical and biotech ecosystem at the University of Minnesota, providing many opportunities for collaboration and access to shared equipment and expertise. The Medical School, College of Pharmacy, Masonic Cancer Center, and Institute for Engineering in Medicine are directly across the street, and their associated core facilities are readily accessible to CEMS researchers. The Biomedical Discovery District, located within a 10 minute walk, houses the Stem Cell Institute and the Center for Immunology, along with other institutes and core facilities that our researchers engage with. The Characterization Facility and the Minnesota Nano Center are also allocated just north of our building. The St. Paul campus, a short shuttle ride away, houses the College of Veterinary Medicine, The Center for Genome Engineering, the BioTechnology Institute, and Molecular and Cellular Therapeutics, which houses GMP biomanufacturing facilities.
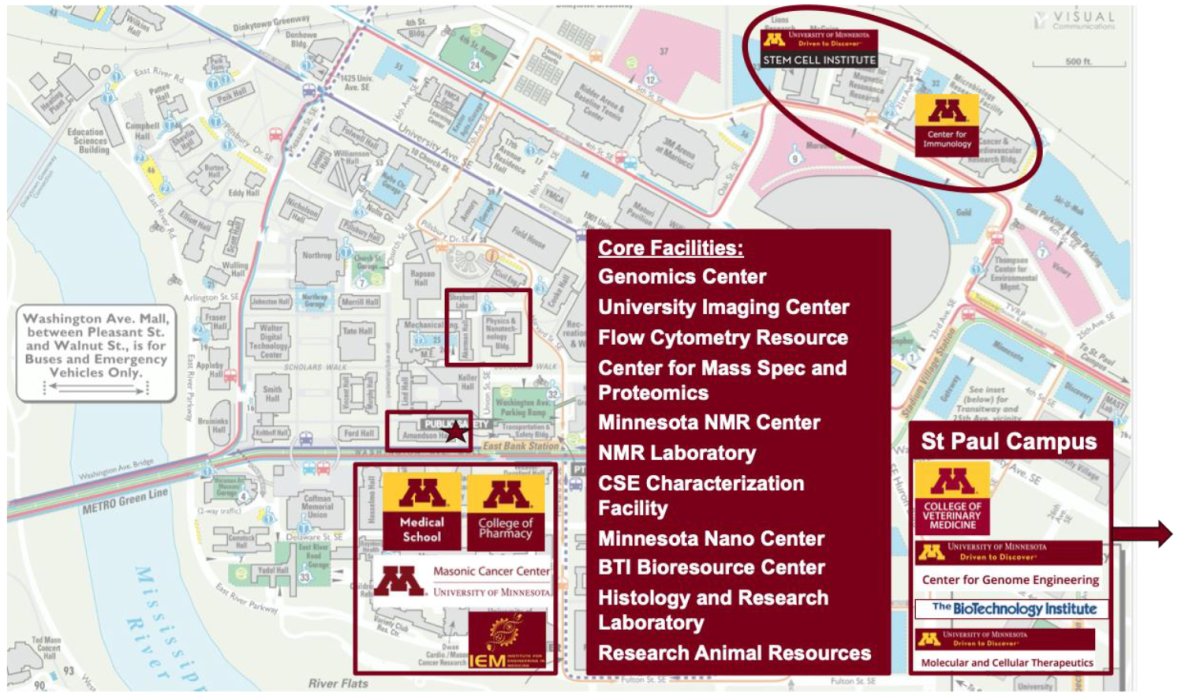
Core Facilities: Genomics Center, University Imaging Center, Flow Cytometry Resource, Center for Mass Spec and Proteomics, Minnesota NMR Center, NMR Laboratory, CSE Characterization Facility, Minnesota Nano Center, BTI Bioresource Center, Histology and Research Laboratory, Research Animals Resources
Major Funding Sources
Publications and Patents
+
Kinetic-model‐based pathway optimization with application to reverse glycolysis in mammalian cells
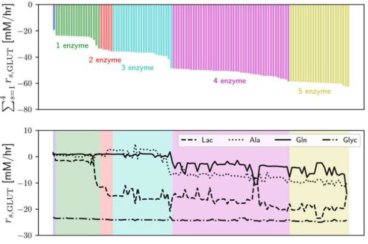
This study developed a two-stage pathway optimization framework based on kinetic metabolic models in order to identify enzyme adjustments that eliminated the need for glucose feed in late stage mammalian culture and improved process robustness. Read More...
Related Faculty:
Wei-Shou Hu- Hu Research Group
Qi Zhang- Zhang Research Group
+
Polysorbate identity and quantity dictate the extensional flow properties of protein- excipient solutions
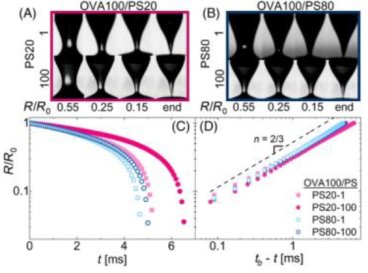
This study developed a methodology to assess extensional flow properties of protein-excipient formulations to address the challenges of identifying protein therapeutic formulations that can achieve injection stability at high concentrations. Read more...
Related Faculty:
Michelle Calabrese- Calabrese Research Group
+
Model-guided engineering of DNA sequences with predictable site-specific recombination rates
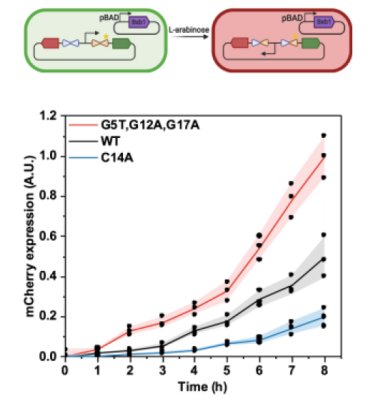
This study combines high throughput experiments with a machine learning model to predict which modifications to a DNA sequence can control the rate of site-specific recombination, enabling differential kinetic regulation of the expression of multiple proteins within a cell by the same enzyme for applications in bacterial therapeutics. Read more...
Related Faculty:
+
A Platform for Deep Sequence–Activity Mapping and Engineering Antimicrobial Peptides
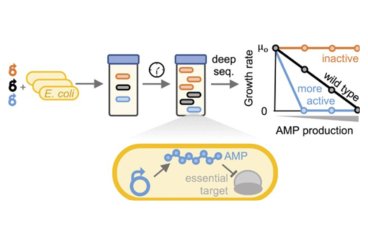
Developing potent antimicrobials, and platforms for their study and engineering, is critical as antibiotic resistance grows. A high-throughput method to quantify antimicrobial peptide and protein (AMP) activity across a broad continuum would be powerful to elucidate sequence–activity landscapes and identify potent mutants. Read More...
Related Faculty:
+
Engineered protein-small molecule conjugates empower selective enzyme inhibition
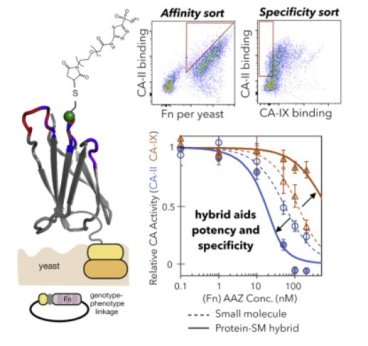
Potent, specific ligands drive precision medicine and fundamental biology. Proteins, peptides, and small molecules constitute effective ligand classes. Yet greater molecular diversity would aid the pursuit of ligands to elicit precise biological activity against challenging targets. Read More...
Related Faculty:
+
Sonosensitizer-Functionalized Graphene Nanoribbons for Adhesion Blocking and Sonodynamic Ablation of Ovarian Cancer Spheroids

This study involved design of graphene-based nanomaterials that bind to metastatic ovarian cancer cells to prevent them from adhering to the lining of the abdominal cavity. In addition, functionalization of the biomaterial with a small molecule sonosensitizer enabled killing of the ovarian cancer cells bound to the material via ultrasound treatment. Read More...
Related Faculty:



